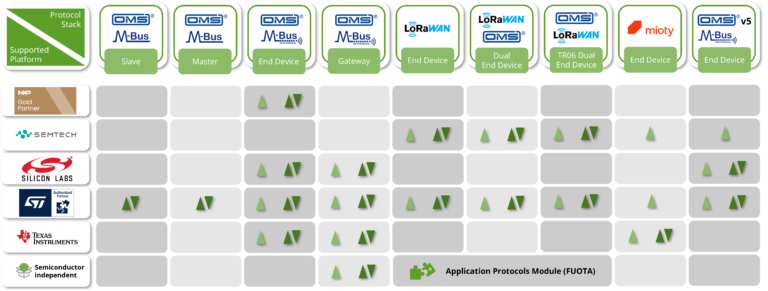
Microcontrollers, Transceivers & System-on-Chip Platforms
The Wireless M‑Bus Stack has already been ported to a wide range of hardware platforms. These include setups consisting of a microcontroller (MCU) paired with a dedicated transceiver (TRX), as well as fully integrated System‑on‑Chip (SoC) solutions. The overview below provides a general impression of the types of hardware suitable for enabling Wireless M‑Bus functionality.
Our list continues to grow with each customer project. If your preferred hardware platform is not included, feel free to contact us – we will evaluate the options with you.

Hardware requirements for the Protocol Stack
To operate reliably on different hardware platforms, the Wireless M‑Bus Stack includes a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL). This layer connects all required hardware components to the protocol stack. Depending on the chosen design, the HAL integrates:
- 1–2 timers
- 1× SPI interface (for dedicated transceiver-based solutions)
- 2–4 GPIOs (depending on the transceiver)
- Software RF interface (for System‑on‑Chip platforms)
- AES encryption in hardware (if available and applicable)
- CRC hardware calculation (if available and applicable)
- Hardware coding support (Manchester, 3oo6 – if available and applicable)
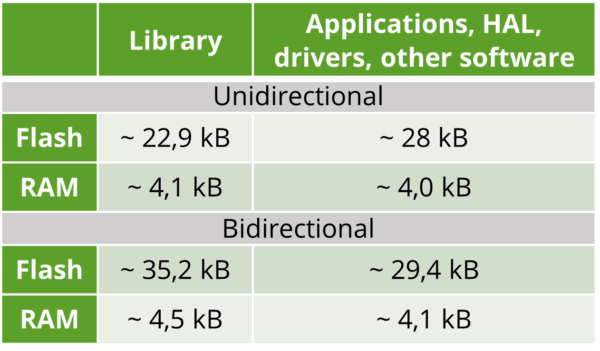
Memory footprint: OMS v4.5.1 End Device Stack, STM32WL5/WLE5
Product Certification – Reliability for Manufacturers & Users
Relying on established standards such as OMS is highly recommended when developing Wireless M‑Bus products. Certification assures all market participants that devices comply with defined norms and interoperability requirements.
OMS certification primarily guarantees cross‑vendor compatibility. For example, an OMS‑certified wM‑Bus receiver from one manufacturer can reliably read data from any OMS‑certified meter, regardless of the vendor.
The OMS certification process is carried out together with DVGW CERT or VDE PZI.
For the Wireless M‑Bus Stack provided by STACKFORCE, certification readiness means that we integrate RF test functions into each of our stacks. These special test modes allow certification bodies – such as TÜV – to validate that the device operates within legal radio specifications. Once the product passes these tests, it can receive the appropriate certification seal.